|
Email / Github / Xiaohongshu |

|
|
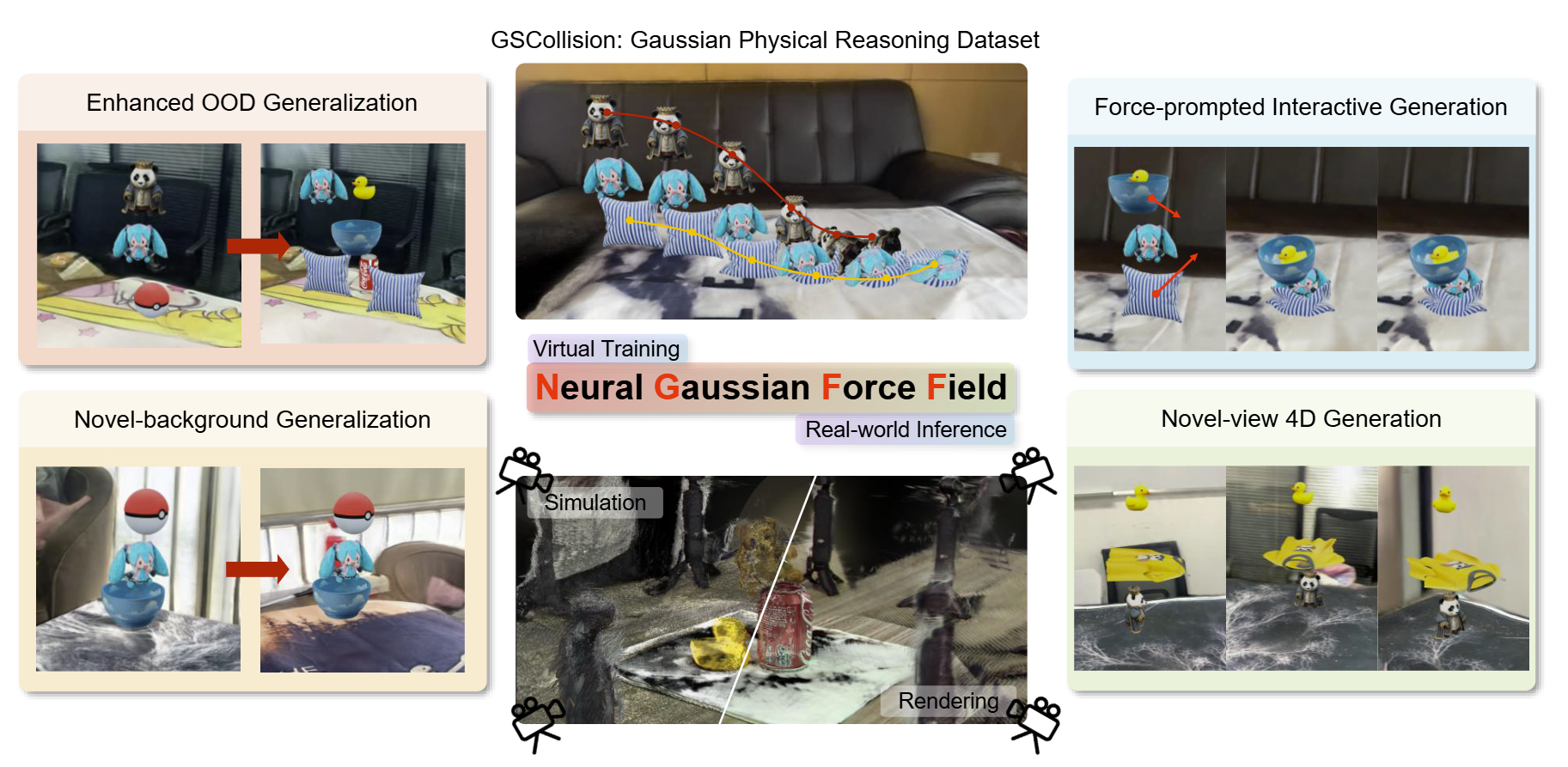
Learning Physics-Grounded 4D Dynamics with Neural Gaussian Force Fields Shiqian Li*, Ruihong Shen*, Junfeng Ni, Chang Pan, Chi Zhang†, Yixin Zhu† PDF / Project Page / OpenReview / Video / Github / Dataset ICLR 2026 Predicting physical dynamics from visual data remains a fundamental challenge in AI, as it requires both accurate scene understanding and robust physics reasoning. While recent video generation models achieve impressive visual quality, they lack explicit physics modeling and frequently violate fundamental laws like gravity and object permanence. Existing approaches combining 3D Gaussian splatting with traditional physics engines achieve physical consistency but suffer from prohibitive computational costs and struggle with complex real-world multi-object interactions. The key challenge lies in developing a unified framework that learns physics-grounded representations directly from visual observations while maintaining computational efficiency and generalization capability. Here we introduce NGFF, an end-to-end neural framework that learns explicit force fields from 3D Gaussian representations to generate interactive, physically realistic 4D videos from multi-view RGB inputs, achieving two orders of magnitude speedup over prior Gaussian simulators. Through explicit force field modeling, NGFF demonstrates superior spatial, temporal, and compositional generalization compared to SOTA methods, including Veo3 and NVIDIA Cosmos, while enabling robust sim-to-real transfer. Comprehensive evaluation on our GSCollision dataset---640k rendered physical videos (~4TB) spanning diverse materials and complex multi-object interactions---validates NGFF's effectiveness across challenging scenarios. Our results demonstrate that NGFF provides an effective bridge between visual perception and physical understanding, advancing video prediction toward physics-grounded world models with interactive capabilities. |
|
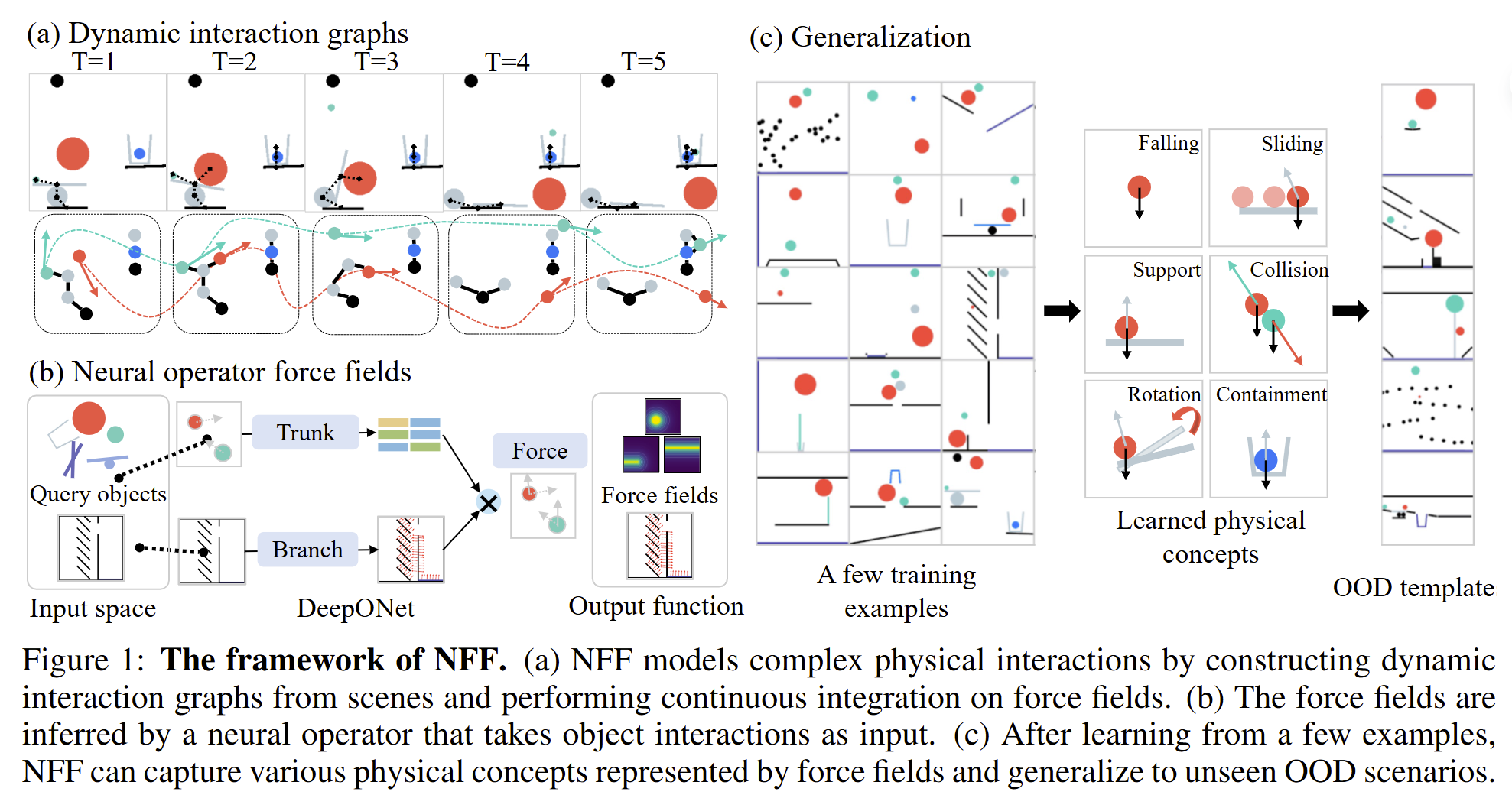
Neural Force Field: Few shot learning of generalized physical reasoning Shiqian Li*, Ruihong Shen*, Yaoyu Tao† Chi Zhang†, Yixin Zhu† PDF / Project Page / OpenReview / Video / Github ICLR 2026 We present NFF, a modeling framework built on NODE that learns interpretable force field representations which can be efficiently integrated through an ODE solver to predict object trajectories. Unlike existing approaches that rely on high-dimensional latent spaces, NFF captures fundamental physical concepts such as gravity, support, and collision in an interpretable manner. Experiments on two challenging physical reasoning tasks demonstrate that NFF, trained with only a few examples, achieves strong generalization to unseen scenarios. This physics-grounded representation enables efficient forward-backward planning and rapid adaptation through interactive refinement. |
|
2025 Spring Instructor: Prof. Bin Chen |
 |
2024.03 - Present Student Research Intern |
 |
Zhi Class (智班)
Honors program initiated by Prof. Baoquan Chen 2023.09 - Present |
 |
2023.09 - Present Undergraduate Student Major: Intelligence Science and Technology (Artificial Intelligence) Double Major: Psychology |
|
|
|
❮
❯
|
|
|